 Javascript validator
Javascripts
Javascript validator
Javascripts
|
|
12.1 Updating with SQLThe simplest way to update the database is to generate a SQL Insert, Update, or Delete statement, and execute it using the Command object's ExecuteNonQuery method. For example, you can insert a few records into the Bugs table, edit existing rows, and delete rows, all with the appropriate SQL statements. To illustrate this, you'll use Visual Studio to create a simple form to display the current records in a grid. Choose whichever language you feel most comfortable using, and name the project BugHistoryHandEdits. In addition to the DataGrid control, you'll add three buttons to allow the user to add, edit, or delete a record, and you'll also add a text field for the description, as shown in Figure 12-1. Table 12-1 shows the properties that you should set for the example to work. Figure 12-1. The data entry page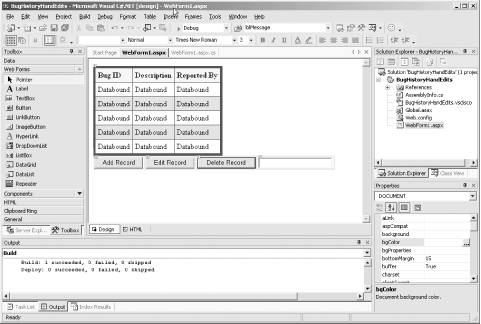
The .aspx file for both C# and VB.NET should now have code similar to the following between the <form> and </form> tags: <asp:DataGrid id="DataGrid1" runat="server" Width="320px" AutoGenerateColumns="False"
BorderWidth="4px" BorderColor="Blue">
<AlternatingItemStyle BorderWidth="4px" BorderStyle="Solid"
BorderColor="Blue" BackColor="LightGray"></AlternatingItemStyle>
<HeaderStyle Font-Bold="True" BackColor="BlanchedAlmond">
</HeaderStyle>
<Columns>
<asp:BoundColumn DataField="BugID"
HeaderText="Bug ID"></asp:BoundColumn>
<asp:BoundColumn DataField="Description"
HeaderText="Description"></asp:BoundColumn>
<asp:BoundColumn DataField="reporter"
HeaderText="Reported By"></asp:BoundColumn>
</Columns>
</asp:DataGrid>
<asp:Button id="btnAdd" runat="server"
Text="Add Record" Width="100px"></asp:Button>
<asp:Button id="btnEdit" runat="server"
Text="Edit Record" Width="100px"></asp:Button>
<asp:Button id="btnDelete" runat="server"
Text="Delete Record" Width="100px"></asp:Button>
<asp:TextBox id="TxtDescription" runat="server" Width="150px"></asp:TextBox>
Next, you'll write Click event handlers for the buttons, and in these event handlers you will interact with the database, executing the SQL statements needed to add a record, edit a record, or delete a record. To simplify the user interface even further, you'll always edit or delete the last record in the table. (In a real application, of course, the user would indicate which record to modify.) The complete C# source code is shown in Example 12-1, and the complete VB.NET source code is shown in Example 12-2. Code not automatically generated by Visual Studio .NET is shown in boldface. Note that, to keep the example as simple as possible, the code has no error checking. Example 12-1. C# source for the data entry pageusing System; using System.Collections; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.Drawing; using System.Text; using System.Web; using System.Web.SessionState; using System.Web.UI; using System.Web.UI.WebControls; using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls; namespace BugHistoryHandEdits { public class WebForm1 : System.Web.UI.Page { // the three buttons protected System.Web.UI.WebControls.Button btnAdd; protected System.Web.UI.WebControls.Button btnEdit; protected System.Web.UI.WebControls.Button btnDelete; // text box to get user input protected System.Web.UI.WebControls.TextBox TxtDescription; // the data grid to display the contents of the bug table protected System.Web.UI.WebControls.DataGrid DataGrid1; public WebForm1( ) { Page.Init += new System.EventHandler(Page_Init); } // when you load the page bind the data from the db private void Page_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { BindData( ); } // bind the grid to the DataReader produced by // the sproc and then update the data private void BindData( ) { DataGrid1.DataSource = CreateBugDataReader( ); DataGrid1.DataBind( ); } // return a DataReader object based on the sproc private SqlDataReader CreateBugDataReader( ) { // connection string to connect to the Bugs Database string connectionString = "server=YourServer; uid=sa; pwd=YourPassword; database=ProgASPDotNetBugs"; // Create connection object, initialize with // connection string. Open it. System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection connection = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection( connectionString); connection.Open( ); // Create a SqlCommand object and assign the connection System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand command = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand( ); command.Connection = connection; // set the stored procedure to get the bug records command.CommandText = "spBugsNoHistory"; command.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure; // return the data reader return command.ExecuteReader( CommandBehavior.CloseConnection); } private void Page_Init(object sender, EventArgs e) { InitializeComponent( ); } #region Web Form Designer generated code /// <summary> /// Required method for Designer support - do not modify /// the contents of this method with the code editor. /// </summary> private void InitializeComponent( ) { this.btnAdd.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.btnAdd_Click); this.btnEdit.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.btnEdit_Click); this.btnDelete.Click += new System.EventHandler(this.btnDelete_Click); this.Load += new System.EventHandler(this.Page_Load); } #endregion // event handler for the edit button // edit the last record based on the user's input private void btnEdit_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { string cmd = @"Update bugs set description = '" + TxtDescription.Text + @"' where bugid = (select max(BugID) from bugs)"; UpdateDB(cmd); BindData( ); } // delete the last record in the table private void btnDelete_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { string cmd = @"delete from bugs where bugid = (select max(BugID) from bugs)"; UpdateDB(cmd); BindData( ); } // add a new record to the table // pick up the description field from the text box private void btnAdd_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { string cmd = @"Insert into bugs values (1,'0.1', '" + TxtDescription.Text + @"',1)"; UpdateDB(cmd); BindData( ); } // common routine for all database updates private void UpdateDB(string cmd) { // connection string to connect to the Bugs Database string connectionString = "server=YourServer; uid=sa; pwd=YourPassword; database=ProgASPDotNetBugs"; // Create connection object, initialize with // connection string. Open it. System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection connection = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection(connectionString); connection.Open( ); // Create a SqlCommand object and assign the connection System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand command = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand( ); command.Connection = connection; command.CommandText = cmd; // clear the text box TxtDescription.Text = ""; // execute the sproc command.ExecuteNonQuery( ); } } } Example 12-2. VB.NET source for the data entry pageImports System.Data.SqlClient Public Class WebForm1 Inherits System.Web.UI.Page Protected WithEvents DataGrid1 As System.Web.UI.WebControls.DataGrid Protected WithEvents btnAdd As System.Web.UI.WebControls.Button Protected WithEvents btnEdit As System.Web.UI.WebControls.Button Protected WithEvents btnDelete As System.Web.UI.WebControls.Button Protected WithEvents TxtDescription As System.Web.UI.WebControls.TextBox #Region " Web Form Designer Generated Code " 'This call is required by the Web Form Designer. <System.Diagnostics.DebuggerStepThrough( )> _ Private Sub InitializeComponent( ) End Sub Private Sub Page_Init(ByVal sender As System.Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Init 'CODEGEN: This method call is required by the Web Form Designer 'Do not modify it using the code editor. InitializeComponent( ) End Sub #End Region Private Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As System.Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load BindData( ) End Sub ' bind the grid to the DataReader produced by ' the sproc and then update the data Private Sub BindData( ) DataGrid1.DataSource = CreateBugDataReader( ) DataGrid1.DataBind( ) End Sub ' return a DataReader object based on the sproc Private Function CreateBugDataReader( ) As SqlDataReader ' connection string to connect to the Bugs Database Dim connectionString As String = _ "server=YourServer; uid=sa; pwd=YourPassword; " & _ "database=ProgASPDotNetBugs" ' Create connection object, initialize with ' connection string. Open it. Dim connection As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection(connectionString) connection.Open( ) ' Create a SqlCommand object and assign the connection Dim command As New SqlCommand( ) command.Connection = connection ' set the stored procedure to get the bug records command.CommandText = "spBugsNoHistory" command.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure ' return the data reader Return command.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection) End Function ' event handler for the edit button ' edit the last record based on the user's input Private Sub btnEdit_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnEdit.Click Dim cmd As String = "Update bugs set description = '" & _ TxtDescription.Text & _ "' where bugid = (select max(BugID) from bugs)" UpdateDB(cmd) BindData( ) End Sub ' delete the last record in the table Private Sub btnDelete_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnDelete.Click Dim cmd As String = _ "delete from bugs where bugid = (select max(BugID) from bugs)" UpdateDB(cmd) BindData( ) End Sub ' add a new record to the table ' pick up the description field from the text box Private Sub btnAdd_Click(ByVal sender As Object, _ ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnAdd.Click Dim cmd As String = "Insert into bugs values (1,'0.1', '" & _ TxtDescription.Text + "',1)" UpdateDB(cmd) BindData( ) End Sub ' common routine for all database updates Private Sub UpdateDB(ByVal cmd As String) ' connection string to connect to the Bugs Database Dim connectionString As String = _ "server=YourServer; uid=sa; pwd=YourPassword; " & _ "database=ProgASPDotNetBugs" ' Create connection object, initialize with ' connection string. Open it. Dim connection As SqlConnection = New SqlConnection(connectionString) connection.Open( ) ' Create a SqlCommand object and assign the connection Dim command As New SqlCommand( ) command.Connection = connection command.CommandText = cmd ' clear the text box TxtDescription.Text = "" ' execute the sproc command.ExecuteNonQuery( ) End Sub End Class For each of the three event handlers for the Click event, you will want to execute the same steps:
All three event handlers require identical steps 2 through 4, so this work is factored out into a common method, UpdateDB, to which you pass the command string you want executed. The syntax of the UpdateDB method in C# is: private void UpdateDB(string cmd) In VB.NET, it is: Private Sub UpdateDB(cmd As String) You create your connection string and connection object as you have in previous examples. You then set the command object's CommandText property to the string passed in as a parameter and execute the query with the ExecuteNonQuery method: command.CommandText=cmd; command.ExecuteNonQuery( ); Remember that ExecuteNonQuery, as you saw in Chapter 11, is used when you do not expect to get back a result set. The return value of ExecuteNonQuery is the number of records affected. The SQL statement for adding a record is a simple Insert statement. In this example, you'll hardwire the values for the Product, Version, and Reporter fields, but you'll pick up the text for the Description field from the text box: string cmd = @"Insert into bugs values (1,'0.1', '" + TxtDescription.Text + @"',1)";
You pass this cmd string to the UpdateDB method as described previously, and then you update the label with the number of rows affected. Finally, you call BindData, which rebinds the data grid with data from the database, and updates the label to display your progress. int numRowsAdded = UpdateDB(cmd); lblMessage.Text = "Added " + numRowsAdded.ToString( ) + " rows."; BindData( ); The three event handlers are identical except for the particular SQL statement executed. The call to BindData rebinds the data grid to the data extracted from the database. BindData in turn calls CreateBugDataReader, which creates an SqlDataReader from the result set returned by the spBugsNoHistory stored procedure. This is a simple stored procedure to retrieve only the few fields from Bugs, lkProduct, and People that we care about for this example program: CREATE PROCEDURE spBugsNoHistory as Select b.BugID, b.Description,p.ProductDescription, r.FullName as reporter from bugs b join lkProduct p on b.Product = p.ProductID join People r on b.Reporter = r.PersonID |
|
|
 Javascript validator
Javascripts
Javascript validator
Javascripts